Can Microbiome Composition in Our Bodies Predict Disease Risk?
Discover how microbiome composition can predict disease risk. Explore the latest research and findings on this fascinating topic.
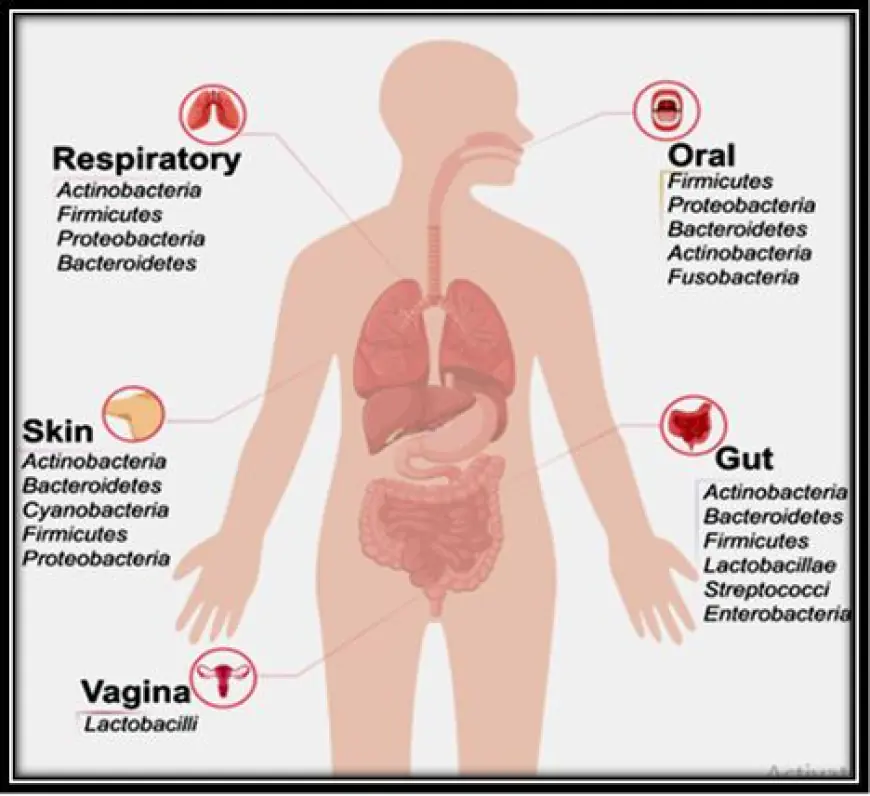
What is the microbiome?
The microbiome is a vast and diverse community of microorganisms residing in our bodies, playing a crucial role in our overall health. It consists of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes that colonize various parts of the body such as the gut, skin, and mouth. This complex ecosystem interacts with our immune system, metabolism, and even brain function. Recent research indicates that the microbiome can influence numerous aspects of human health including digestion, nutrient absorption, and even mental well-being.
Moreover, it's fascinating to note that each individual's microbiome is unique and can change over time due to factors like diet, environment, and medical treatments. The balance of different microbial species in the microbiome is part of what makes it so influential in determining one's susceptibility to certain diseases or disorders. Understanding this intricate interplay between our bodies' microbial inhabitants and their impact on disease risk opens up exciting possibilities for personalized medicine tailored to an individual's specific microbiome composition.
The link between microbiome and disease
The link between microbiome and disease is a burgeoning area of research that has the potential to revolutionize healthcare. Over the past decade, numerous studies have shed light on how the trillions of microorganisms inhabiting our bodies can influence our susceptibility to various diseases. From autoimmune disorders to obesity and even mental health issues, it's becoming increasingly clear that the microbiome plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health. The composition of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microorganisms in our gut could potentially serve as an early warning system for certain diseases, offering a window into our future health trajectory.
One fascinating aspect of this research is the concept of microbial diversity and its impact on disease risk. Studies have suggested that individuals with lower microbial diversity in their gut may be more prone to developing certain illnesses compared to those with a richer array of microorganisms. This has led researchers to explore ways of manipulating the microbiome to restore balance and mitigate disease risk. In essence, understanding the intricate interplay between our body's microbial communities and disease development holds promise for personalized medicine approaches aimed at preventing, diagnosing, and treating a range of conditions through targeted interventions tailored to individual microbiome profiles.
Research findings on disease prediction
As scientists delve deeper into the world of microbiome research, intriguing findings on disease prediction continue to emerge. Recent studies have revealed that the composition of microorganisms in our bodies may hold the key to predicting disease risk. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine found that variations in gut microbial diversity were associated with an increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. This suggests that analyzing the microbiome could potentially serve as a predictive tool for identifying individuals at higher risk for these conditions.
Moreover, research has indicated that alterations in the vaginal microbiota could potentially be used to predict gynecological conditions such as bacterial vaginosis and cervical cancer. A study from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health demonstrated that certain microbial profiles were linked to an elevated risk of developing these conditions, paving the way for innovative methods of early detection and personalized preventive interventions. These discoveries open up new possibilities for leveraging microbiome data to forecast disease susceptibility, leading us toward more targeted and proactive healthcare strategies based on individual microbial signatures.
The fascinating implications of these research findings offer a glimpse into a future where personalized medicine is not just a concept but a reality built on the intricate dynamics of our microbiomes. As we continue unraveling this uncharted territory, integrating microbiome data into disease prediction models holds tremendous promise for improving public health outcomes and revolutionizing how we approach preventive care.

Factors influencing microbiome composition
The composition of the microbiome in our bodies is influenced by a myriad of factors, and researchers are only starting to scratch the surface of understanding this complex relationship. Diet plays a critical role in shaping the microbiome, with studies revealing that a high-fiber diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote a more diverse and beneficial microbial community. Additionally, environmental factors such as pollution and exposure to antibiotics have been shown to alter the composition of the microbiome, potentially leading to dysbiosis and associated health problems.
Moreover, emerging evidence suggests that psychological stress can also impact our microbiome composition. Stress-induced changes in gut permeability may lead to alterations in microbial diversity and function, highlighting the intricate interplay between mental health and gut health. Furthermore, recent studies have uncovered the influence of genetics on microbiome composition, emphasizing individual differences in how our bodies harbor microbial communities. These findings underscore the multifaceted nature of microbiome dynamics and its potential relevance for predicting disease risk.
Potential implications for personalized medicine
The potential implications of personalized medicine in the context of microbiome composition are staggering. With a better understanding of how individual microbiomes influence disease risk, personalized interventions and treatments could be developed. This would mean tailoring medical approaches to an individual's specific microbiome profile, potentially leading to more effective and targeted healthcare.
Moreover, the integration of microbiome data into personalized medicine could revolutionize disease prevention strategies. By identifying specific microbial signatures associated with disease risk, healthcare providers could offer proactive interventions to mitigate these risks before symptoms even develop. This shift from reactive to proactive healthcare has the potential to significantly improve health outcomes for individuals and reduce the burden on healthcare systems.
Ethical considerations and future directions
When delving into the realm of microbiome research, it is crucial to address the ethical considerations that come into play. With the potential for microbiome composition to predict disease risk, researchers must navigate questions around privacy, informed consent, and data security. While the promise of personalized medicine is exciting, it's essential to ensure that ethical guidelines are in place to protect individuals' rights and autonomy.
Looking towards future directions in this field, there are vast opportunities for groundbreaking discoveries and advancements. As technology continues to evolve, we can anticipate more sophisticated methods for analyzing microbiome data and uncovering novel insights. Moreover, integrating microbiome research with other omics disciplines such as genomics and proteomics holds great potential for a comprehensive understanding of human health and disease. The future also presents an opportunity for interdisciplinary collaboration between scientists, clinicians, ethicists, and policymakers to shape responsible practices that harness the full potential of microbiome research while upholding ethical standards.
Conclusion: Harnessing microbiome for health predictions
In conclusion, the burgeoning field of microbiome research holds tremendous potential for predicting health outcomes and disease risks. By leveraging the diverse community of microorganisms that inhabit our bodies, scientists can gain valuable insights into individual health and susceptibility to various medical conditions. The intricate interplay between the microbiome and human physiology underscores the need for further exploration to unlock its predictive power.
As we peer into this microbial world within us, it becomes increasingly evident that harnessing the microbiome for health predictions could revolutionize personalized medicine. By parsing through the complex interactions between microbial populations and an individual's genetic predispositions, researchers are inching closer to developing innovative diagnostic tools that could forewarn individuals of potential health challenges long before symptoms arise. Embracing this frontier of science may pave the way for a new era where proactive healthcare interventions tailored to an individual's unique microbial profile become commonplace, ultimately transforming how we approach disease prevention and management.







